Margaret Thatcher: The Iron Lady Who Transformed Global Politics
Discover the life and legacy of Margaret Thatcher, the pioneering British Prime Minister whose bold policies reshaped the UK and influenced the global economy.
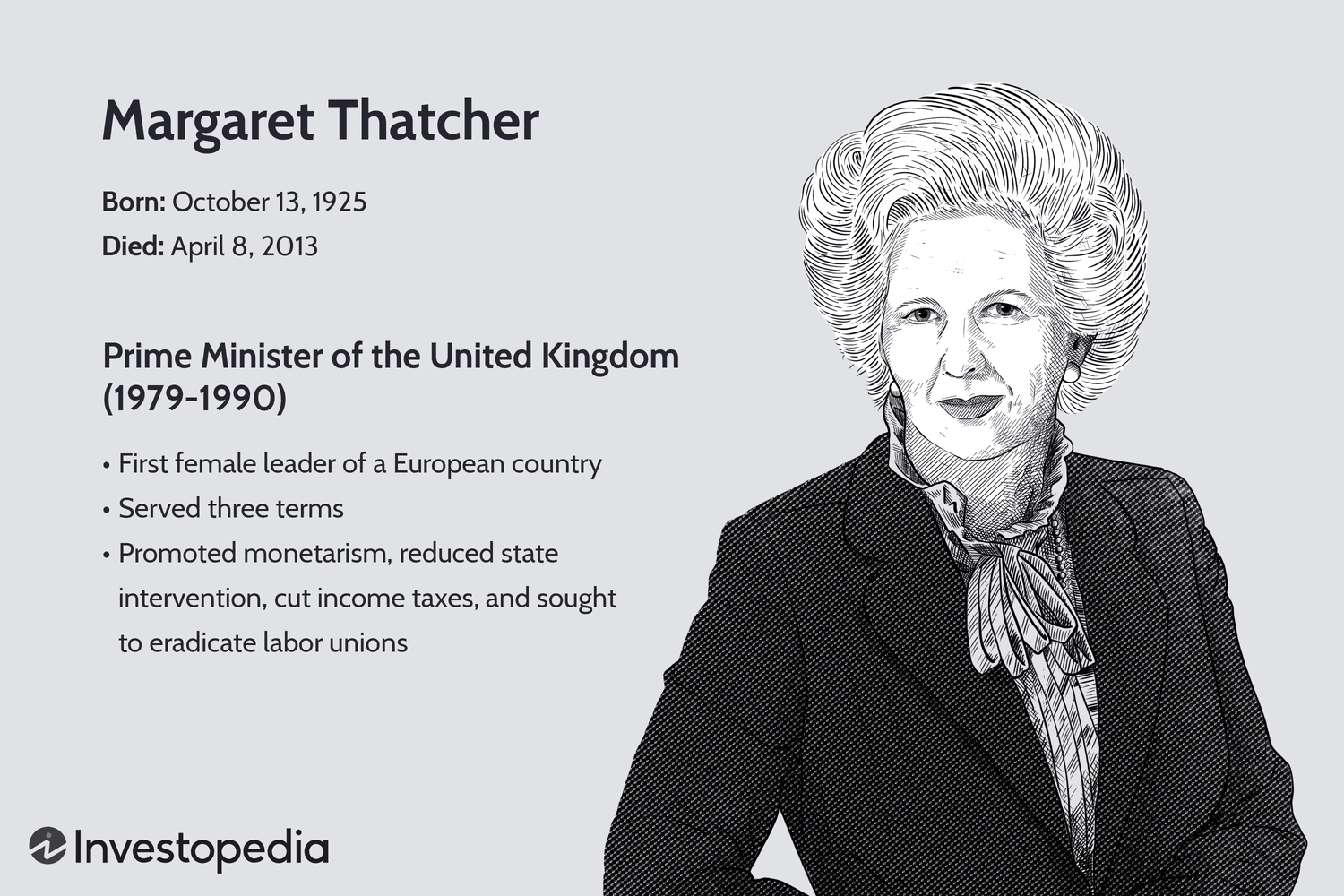
Margaret Thatcher, famously known as the Iron Lady, was a trailblazing British political leader whose transformative policies ignited the global neoliberal movement of the 1980s.
As the first female Prime Minister in Europe, Thatcher governed the United Kingdom for over 11 years, implementing reforms that not only revolutionized Britain’s economic landscape but also left an indelible impact worldwide.
Key Highlights
- Margaret Thatcher played a pivotal role, alongside Ronald Reagan, in ushering in the era of neoliberalism.
- She became the UK's first female Prime Minister in 1979 and held office for more than a decade.
- Her administration prioritized monetarism, minimized government intervention, slashed income taxes, and confronted labor unions.
- Thatcher resigned in 1990 and passed away in 2013, yet her influence remains profound.
- Her legacy continues to shape modern conservative politics and economic policies globally.
Early Life and Academic Pursuits
Born Margaret Hilda Roberts on October 13, 1925, in Grantham, Lincolnshire, England, she was raised in a Methodist household emphasizing self-reliance and community values. Her father, Alfred Roberts, was an active local politician, which sparked her early interest in governance.
At 18, she attended Oxford University to study chemistry, becoming the first woman elected president of the Oxford University Conservative Association. Though passionate about chemistry, politics was her true calling.
From Chemistry to Law and Politics
After university, Thatcher worked as a research chemist at BX Plastics in Essex while actively engaging in politics. She ran unsuccessfully for Parliament in 1950 and 1951 but gained national attention as the youngest female candidate.
She married Denis Thatcher and transitioned to law, specializing in taxation. Her political career accelerated in 1959 when she was elected MP for Finchley, gradually rising through government ranks, including roles as parliamentary secretary and Secretary of State for Education and Science.
In 1975, she became leader of the Conservative Party, and by 1979, amid economic turmoil and labor unrest, she was elected Prime Minister.
Transformative Political Agenda
During her three terms, Thatcher revolutionized Britain's economy, adopting monetarist principles, championing free-market capitalism, and reducing state control.
Privatization and Deregulation
Believing in minimal government interference, Thatcher privatized numerous state-owned enterprises, especially utilities, selling shares to the public and promoting private ownership.
She also deregulated financial markets, attracting international capital and fostering economic growth, though this deregulation later contributed to global financial instability.
Confronting Labor Unions
Thatcher viewed powerful labor unions as obstacles to economic progress. The 1984 miners' strike marked a turning point, with the government prevailing over the unions, leading to stricter laws limiting union power.
Tax Reforms and Social Policies
She drastically reduced the top income tax rate from 83% in 1979 to 40% by 1988, offsetting revenue losses by increasing VAT and introducing a controversial poll tax, which disproportionately affected lower-income citizens.
Promoting Homeownership
The 1980 Housing Act enabled council tenants to buy their homes at discounted rates, encouraging private ownership but also reducing affordable public housing availability.
Enduring Legacy
Margaret Thatcher passed away on April 8, 2013, but her legacy endures. She is credited with revitalizing the British economy, strengthening transatlantic ties with the United States, and shaping modern conservative ideology.
While admired for her decisive leadership, critics highlight the rise in social inequality and her uncompromising style toward opponents.
Later Years and Influence
After stepping down in 1990 due to declining support within her party, Thatcher remained active in politics, authored memoirs, and founded the Margaret Thatcher Foundation. Health issues led to reduced public appearances until her death.
Role in Ending the Cold War
Known for her staunch anti-communism, Thatcher's firm stance against the Soviet Union and her diplomatic engagement with Mikhail Gorbachev contributed to the Cold War's conclusion.
Summary
Margaret Thatcher stands as one of the most influential and polarizing figures of the 20th century. Her pioneering leadership and economic reforms transformed Britain and inspired global shifts toward neoliberal policies that continue to influence the world today.
Discover engaging topics and analytical content in Government & Policy as of 11-04-2022. The article titled " Margaret Thatcher: The Iron Lady Who Transformed Global Politics " provides new insights and practical guidance in the Government & Policy field. Each topic is meticulously analyzed to deliver actionable information to readers.
The topic " Margaret Thatcher: The Iron Lady Who Transformed Global Politics " helps you make smarter decisions within the Government & Policy category. All topics on our website are unique and offer valuable content for our audience.