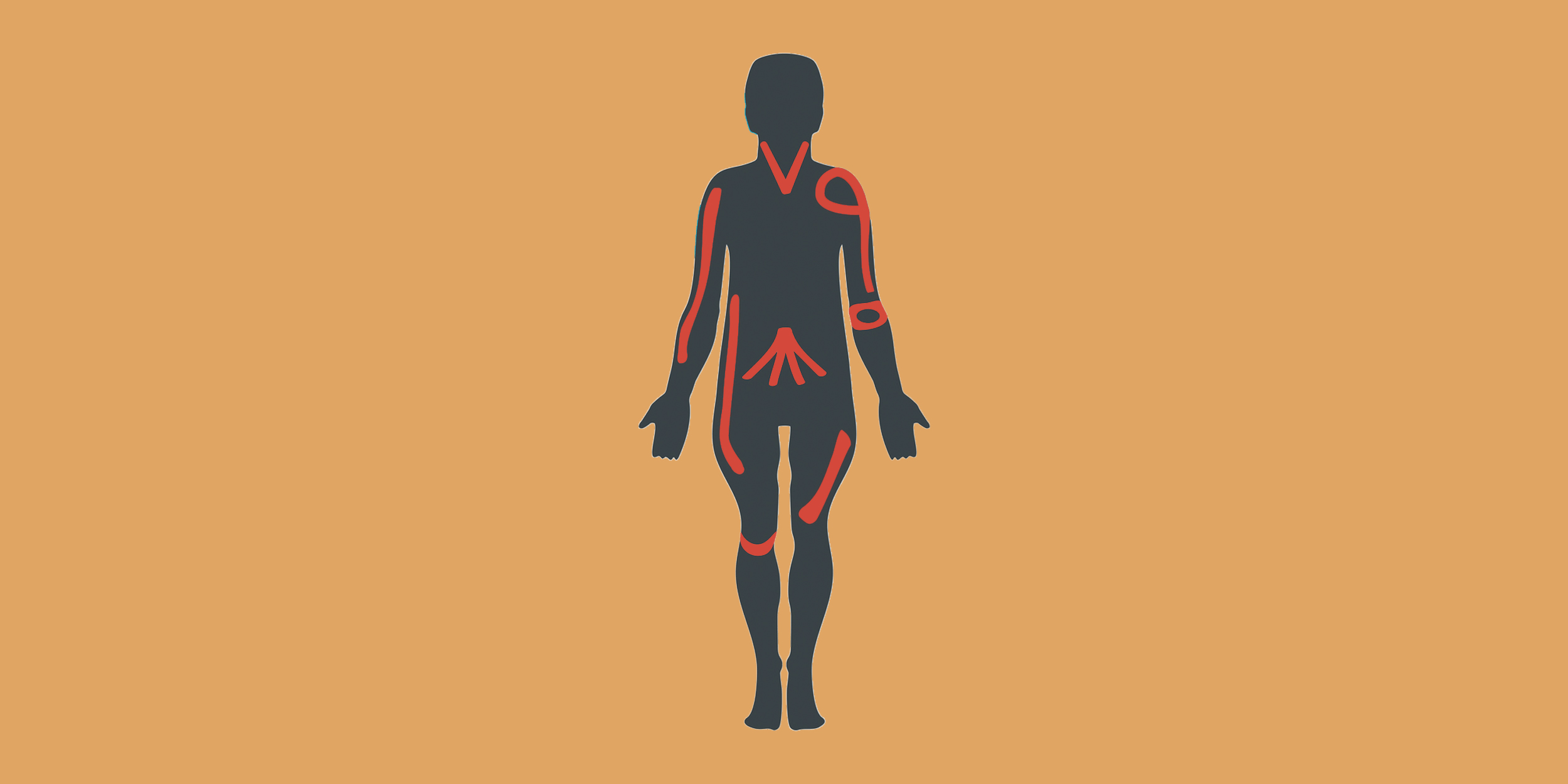
Comprehensive Guide to Gym Injuries: Prevention, Treatment, and Recovery
Explore common gym-related injuries, learn immediate response strategies, understand recovery timelines, and discover effective prevention methods to keep your workouts safe and productive.
This guide delves into typical injuries encountered in the gym, how to prevent them, and what actions to take if injuries occur despite precautions.
Ligament Sprains

Ligaments stretch up to 4% under normal conditions but can partially or completely tear during sudden movements.
Sprains most commonly affect the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and knee ligaments.
Signs and Symptoms
Orthopedic specialist Dr. Oleg Milenin notes that patients often experience no symptoms or pain immediately after a ligament sprain.

Dr. Oleg Milenin
Orthopedic trauma specialist and associate professor at the National Medical and Surgical Center, with a PhD in medical sciences and head of the Sports Medicine Clinic.
Pain and swelling typically develop the following day, intensifying with movement or pressure on the injured area.
Causes
Dr. Milenin explains that ligament sprains often result from impaired proprioception—the body’s ability to sense joint position. Normally, muscles cushion excessive loads through contraction, protecting ligaments.
Fatigue or inadequate preparation disrupts this mechanism, increasing the risk of sprains or ruptures.
Fitness coach Ruslan Pustovoy highlights that sprains frequently occur on treadmills or due to incorrect exercise techniques.

Ruslan Pustovoy
Fitness club instructor and power extreme champion, also an orthopedic trauma specialist.
Immediate Actions
Upon spraining a ligament, stop exercising and immobilize the affected limb. Mild sprains typically resolve within 3–4 days with proper care, including immobilization, anti-inflammatory ointments, and cold therapy, according to Dr. Milenin.
Physical therapy physician Oleg Evdokimov adds that therapeutic exercises with a trainer can sometimes begin the day after injury.

Oleg Evdokimov
Physical therapy and sports medicine physician, trainer at the "Health and Sports" studio.
If pain and swelling persist beyond a few days, consult a doctor promptly. Treatment may involve immobilization with a brace or cast for up to a week, followed by rehabilitation.
Return to Training
Recovery from ligament sprains generally ranges from one week to one month, depending on injury severity, says Ruslan Pustovoy.
Prevention Tips
Dr. Milenin recommends strengthening muscles parallel to the ligaments and focusing on proprioception through balance exercises, such as platform training. Incorporate plyometric exercises for lower limb ligaments and multidirectional, high-speed movements for upper limb ligaments.
Partial Muscle Tears

Dr. Milenin explains that muscle tears occur when muscles contract against the direction of load. Commonly affected muscles include hamstring flexors, Achilles tendon, pectoralis major, and the long head of the biceps tendon.
Symptoms
Partial tears in the muscle belly often cause hematomas, and more extensive tears lead to visible muscle deformity. Pain may not always be present, but prompt medical evaluation is essential.
Causes
Rehabilitation specialist and fitness trainer Andrey Pitirimov notes that muscle tears often result from lifting excessive weights without adequate preparation or prolonged static muscle contraction.

Andrey Pitirimov
Rehabilitation physician and fitness trainer.
For example, improper technique during a clean and press that relies excessively on the biceps can cause muscle tears.
What to Do
Dr. Evdokimov advises:
- Cease training immediately;
- Apply ice to the injured area;
- Immobilize the affected zone;
- Seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment varies with injury severity, ranging from supportive bandages and rehabilitation to surgical repair in severe cases.
Recovery Timeline
Complete rest and pain management are recommended for about 10 days for partial tears. Return to physical activity typically takes at least four weeks, while full tears requiring surgery may need up to six months for recovery.
Prevention Strategies
Dr. Milenin suggests training tendons and ligaments by incorporating exercises that engage both agonist and antagonist muscles simultaneously, along with plyometric and balance training. Collagen supplements may also support tissue resilience during intense training.
Nerve Compression

Andrey Pitirimov explains that nerve roots emerging from the spinal cord can be compressed by muscle spasms, trigger points, or displaced vertebrae due to osteochondrosis.
Symptoms
Nerve compression symptoms vary from numbness and tingling sensations to severe pain.
Causes
Attempting high repetitions with unprepared muscles can provoke muscle spasms leading to nerve entrapment.
Recommended Actions
Medical evaluation is crucial. Treatment may include muscle relaxants, physiotherapy, and massage for muscle-induced compression. Vertebral injuries might require manual therapy, osteopathy, or surgery.
Return to Activity
Recovery depends on the cause; muscle spasms often resolve within 7–10 days, while spinal issues may require extended rehabilitation.
Prevention
Dr. Milenin advises avoiding repetitive flexion-extension movements and preventing microtraumas to joints and ligaments.
Intervertebral Disc Herniation

Intervertebral disc herniation occurs when the fibrous ring surrounding the disc ruptures, allowing the gel-like nucleus pulposus to protrude.
Andrey Pitirimov states that hernias develop over years due to poor posture and disc degeneration, with minor overloads triggering protrusions or herniations.
Most hernias occur in the lumbar-sacral region, less commonly in the cervical, and rarely in the thoracic spine.
Symptoms
Lumbar hernias cause lower back pain radiating to the buttocks or leg. Cervical hernias manifest as neck, shoulder, or head pain, dizziness, tinnitus, or finger numbness. Thoracic hernias cause chest discomfort.
Causes
Sudden, forceful movements with improper technique, such as jerky lifts, can rupture the fibrous ring. Even lifting weights off the floor improperly can lead to injury.
Immediate Care
Dr. Pitirimov recommends lying on a firm surface with soft supports under spinal curves to relieve pain. Emergency transport may be necessary; call emergency services immediately.
Treatment includes NSAIDs, therapeutic exercises, and occasionally surgery. Over time, the nucleus pulposus shrinks, reducing nerve pressure, but future training requires careful load management and core strengthening.
Recovery Period
With effective treatment involving massage, therapy, and spinal traction, recovery may take several months.
Prevention
Dr. Milenin emphasizes exercises that balance spinal disc load and strengthen back and abdominal muscles. Maintaining proper posture during daily activities, especially at work, is also essential.
Dislocations

Dr. Milenin defines dislocation as the complete separation of joint surfaces, while subluxation is a partial displacement.
In gyms, dislocations commonly affect the shoulder and elbow joints, less frequently the knee. "Unfortunately, 95% of young patients experience recurrence after the first dislocation," warns Dr. Milenin.
Symptoms
Dislocations cause joint deformity and swelling, sometimes accompanied by bruising due to vessel and soft tissue damage. Movement causes sharp pain, and passive motion meets resistance. Nerve damage may cause numbness.
Causes
Dislocations often result from lifting excessive weights with poor technique. For example, heavy leg press loads may dislocate the knee, while seated or overhead barbell presses can dislocate the shoulder.
Immediate Response
Immobilize the joint and seek urgent orthopedic care. Dr. Evdokimov explains that reducing a dislocation within 30 minutes can often be done without anesthesia; delays beyond 40 minutes require anesthesia due to muscle rigidity.
Post-reduction rehabilitation includes physiotherapy.
Return to Training
Ruslan Pustovoy advises resuming workouts no sooner than six weeks post-dislocation.
Dr. Milenin notes that associated injuries like labral tears or ligament damage may require arthroscopic surgery with anchor fixation, enabling recovery within approximately four months.
Prevention
Strengthen muscles stabilizing joint surfaces and improve reaction speed to prevent dislocations, recommends Dr. Milenin.
General Injury Prevention Tips
To minimize gym injuries, follow these guidelines:
- Engage in thorough warm-ups and preparatory exercises.
- Gradually increase weights and repetitions.
- Learn new complex movements under professional supervision.
Share your gym injury experiences and recovery stories in the comments below.
*Note: Meta Platforms Inc. and its social networks Facebook and Instagram are restricted in certain regions.
Discover engaging topics and analytical content in Sports and Health as of 26-03-2024. The article titled " Comprehensive Guide to Gym Injuries: Prevention, Treatment, and Recovery " provides new insights and practical guidance in the Sports and Health field. Each topic is meticulously analyzed to deliver actionable information to readers.
The topic " Comprehensive Guide to Gym Injuries: Prevention, Treatment, and Recovery " helps you make smarter decisions within the Sports and Health category. All topics on our website are unique and offer valuable content for our audience.