Put-Call Parity Explained 2025: Formula, Meaning, Arbitrage & Real Examples
Discover the modern interpretation of put-call parity in 2025, the key formula linking European put and call options prices, and how traders use it to spot arbitrage opportunities in today's markets.
Gordon Scott is a seasoned investor and technical analyst with over 20 years of experience, holding the Chartered Market Technician (CMT) designation.
What is Put-Call Parity in 2024?
Put-call parity is a fundamental financial principle that defines the precise relationship between the prices of European call and put options that share the same underlying asset, strike price, and expiration date. It forms the backbone of options pricing theory and is critical for maintaining market efficiency.
In simple terms, the parity asserts that the combined value of holding a call option plus the present value of the strike price (discounted at the risk-free rate) should equal the combined value of holding a put option plus the current price of the underlying asset. Any deviation from this equilibrium signals a pricing inconsistency that savvy traders can capitalize on.
Core Insights to Remember
- Put-call parity strictly applies to European-style options exercisable only at expiration, not American options.
- It establishes a no-arbitrage relationship binding put and call option prices with the underlying asset’s value.
- Discrepancies in this relationship reveal arbitrage opportunities, though such chances are scarce in modern algorithm-driven markets.
- Practical factors like transaction costs, taxes, dividends, and market liquidity can cause slight deviations from theoretical parity.
Understanding the Put-Call Parity Formula
The put-call parity equation is expressed as:
C + PV(x) = P + S
Where:
- C = Price of the European call option
- PV(x) = Present value of the strike price (x), discounted at the risk-free interest rate until expiration
- P = Price of the European put option
- S = Current spot price of the underlying asset
This formula implies that combining a long call option and a discounted cash amount equal to the strike price matches the payoff of holding a long position in the underlying asset plus a put option, maintaining equilibrium in the options market.
Historical Context
The concept of put-call parity was first formalized by economist Hans R. Stoll in his 1969 publication "The Relationship Between Put and Call Option Prices," featured in the Journal of Finance, laying the groundwork for modern options pricing.
Practical Example: Verifying Put-Call Parity in 2024
Imagine a six-month European put option on stock XYZ with a strike price of $55 is trading at $7.46. The stock currently trades at $50, the present value of the strike price discounted at the risk-free rate is $54.46, and the corresponding call option costs $3.00.
Applying the put-call parity formula:
$3.00 + $54.46 = P + $50
$57.46 = P + $50
P = $7.46
The put option price aligns perfectly with the parity value, confirming no arbitrage opportunity.
Identifying Arbitrage When Parity Breaks
If the put option is priced at $8.00 instead of $7.46, the equation becomes:
$3.00 + $54.46 ≠ $8.00 + $50
$57.46 ≠ $58.00
This disparity indicates an overpriced put option. Traders can exploit this by selling the put at $8.00, purchasing the call at $3.00, and shorting the stock at $50, securing an immediate risk-free gain.
Leveraging Put-Call Parity for Arbitrage Strategies
Arbitrageurs profit when the parity relationship is disrupted by executing offsetting trades: selling the overvalued option and buying the undervalued one, often involving shorting or buying the underlying asset and investing in risk-free instruments.
In practice, such opportunities are fleeting due to high-frequency trading and market efficiency. Additionally, tight margins often require significant capital to realize meaningful profits.

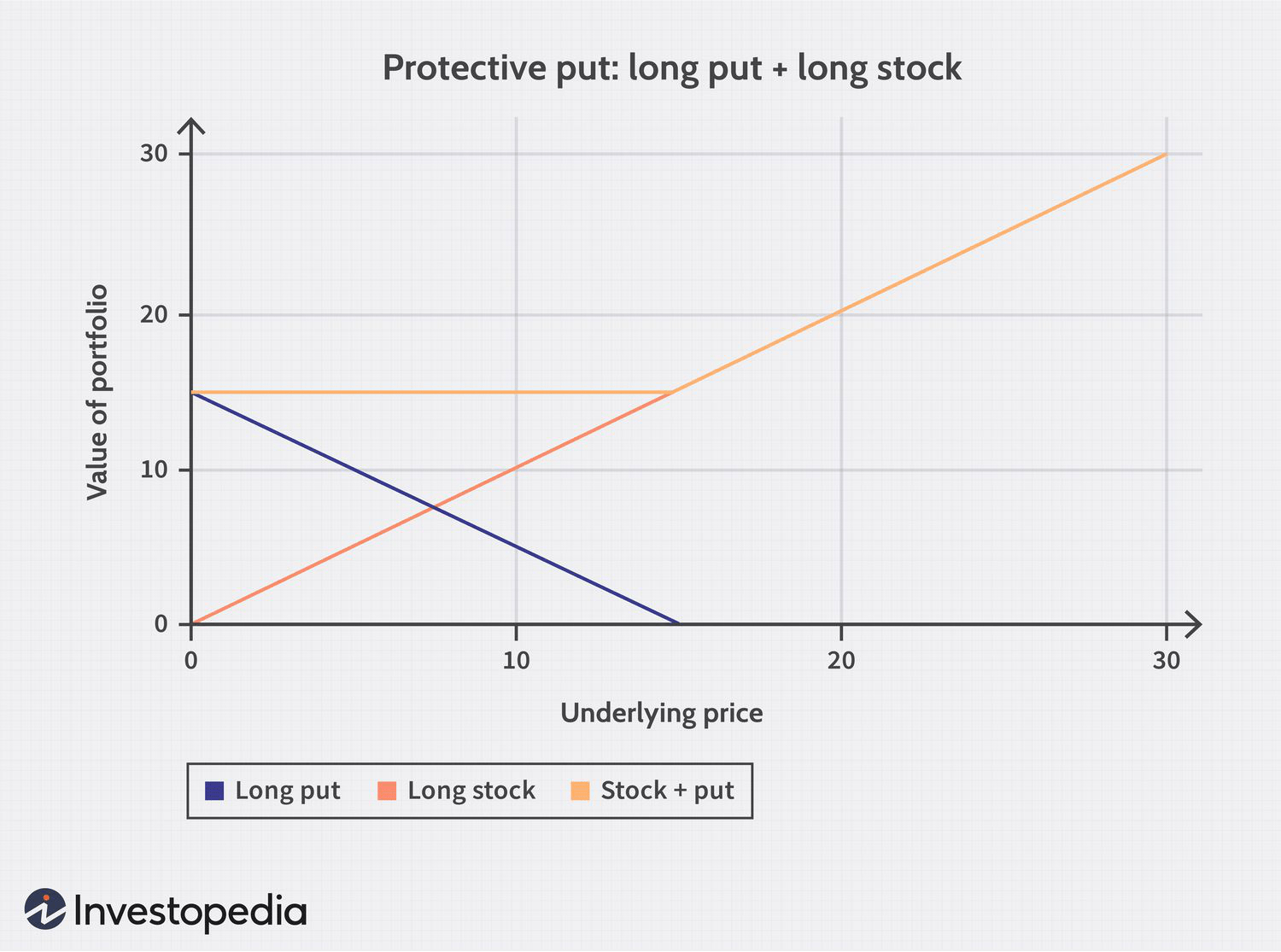
Protective Put vs. Fiduciary Call Explained
Put-call parity also links two popular investment strategies:
- Protective Put: Holding a long position in the underlying stock combined with a long put option to hedge downside risk.
- Fiduciary Call: Holding a long call option with cash or a risk-free asset equal to the present value of the strike price, ensuring funds for exercise at expiration.
Both yield similar payoff profiles, illustrating the deep connection between options and their underlying assets.

Put-Call Parity and American Options: What to Know
While put-call parity is exact for European options, American options introduce complexities due to the possibility of early exercise. Dividends and early exercise premiums may modify the parity relationship, but the foundational principle still guides pricing and arbitrage considerations.
Impact of Dividends and Interest Rates on Parity
Dividends reduce the underlying asset’s price, lowering call option values and increasing put option prices, thus affecting parity calculations. Similarly, rising interest rates tend to increase call premiums and decrease put premiums, reflecting the cost of carry.
How Are Option Prices Determined in 2024?
Options pricing integrates intrinsic value (difference between underlying price and strike) and time value (premium for remaining time until expiration). Advanced mathematical models like Black-Scholes-Merton compute fair values by considering volatility, strike, underlying price, time to expiration, and risk-free rates.
Final Thoughts on Put-Call Parity
Put-call parity remains a cornerstone of options theory in 2024, ensuring a balanced relationship between call and put prices relative to the underlying asset. Understanding this principle empowers traders and investors to recognize pricing inefficiencies, execute arbitrage strategies, and manage risk effectively in European options markets.
Discover the latest news and current events in Options & Derivatives Trading as of 16-06-2024. The article titled " Put-Call Parity Explained 2025: Formula, Meaning, Arbitrage & Real Examples " provides you with the most relevant and reliable information in the Options & Derivatives Trading field. Each news piece is thoroughly analyzed to deliver valuable insights to our readers.
The information in " Put-Call Parity Explained 2025: Formula, Meaning, Arbitrage & Real Examples " helps you make better-informed decisions within the Options & Derivatives Trading category. Our news articles are continuously updated and adhere to journalistic standards.


