2025 Pulse Oximeter Guide: How to Monitor Oxygen Levels at Home with COVID-19
Discover how to effectively use a pulse oximeter at home to monitor oxygen levels during COVID-19, recognize critical signs, and know when to seek medical help.
Using a pulse oximeter to track your oxygen saturation while battling COVID-19 is vital for detecting dangerously low oxygen levels early. Timely intervention can save lives.
COVID-19 primarily affects the respiratory system, potentially causing breathing difficulties and reducing oxygen in your bloodstream. Insufficient oxygen can impair vital body functions and become life-threatening.
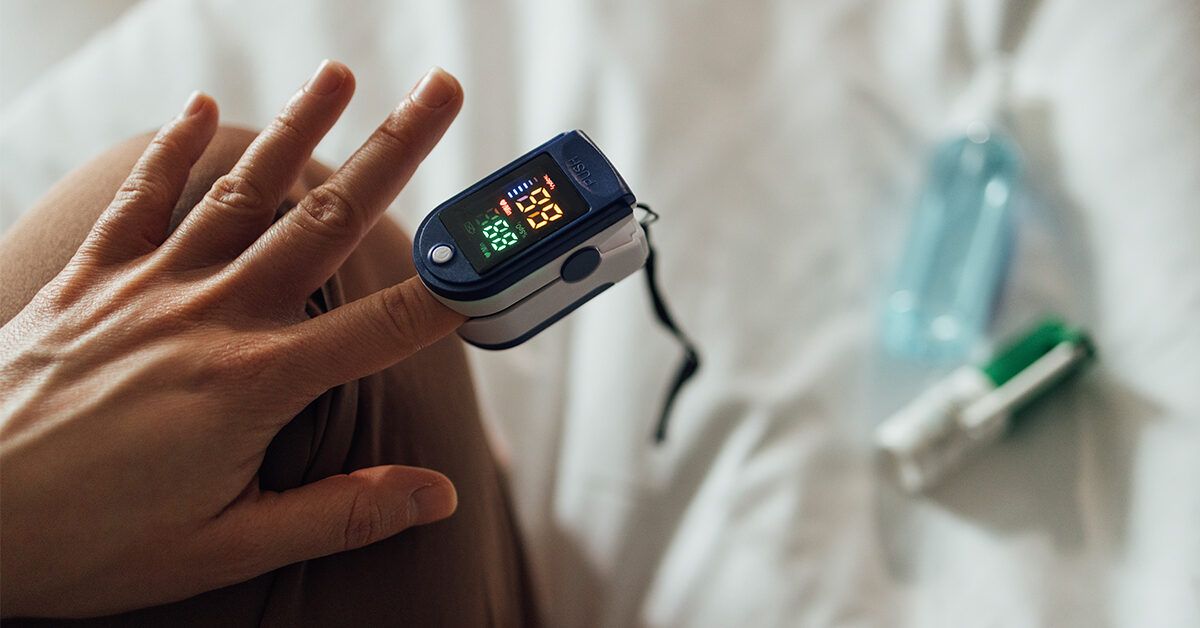
Monitoring your blood oxygen at home with a pulse oximeter—a simple, affordable device—is an effective way to gauge your condition and recovery progress.
This device displays oxygen saturation as a percentage. Readings below 90% indicate the need for immediate medical attention.
Understanding Blood Oxygen Levels
Blood oxygen level measures the oxygen content carried by your red blood cells. When you inhale, oxygen passes through your lungs into your bloodstream. Lung inflammation from COVID-19 can decrease oxygen intake.
Your body requires adequate oxygen to maintain essential functions like heart activity and energy production, which supports thinking, movement, and daily tasks.
Oxygen saturation is expressed as a percentage, with values near 100% signifying optimal oxygen availability.
Safe Oxygen Levels for COVID-19 Patients
A healthy oxygen saturation level is generally 95% or higher. People with chronic lung diseases, such as COPD, may have lower baseline levels.
If you have an existing lung condition and test positive for COVID-19, promptly consult your healthcare provider for tailored monitoring and treatment advice.
Critical Oxygen Thresholds
Oxygen saturation below 90% is dangerously low and warrants urgent medical care.
Home monitoring guidelines include:
- Consult your doctor if oxygen levels drop below 95%
- Seek emergency care if levels fall under 90%
Why Use a Pulse Oximeter During COVID-19?
A pulse oximeter noninvasively measures blood oxygen levels and is commonly used in medical settings. During COVID-19, doctors may recommend home use to detect low oxygen before symptoms like breathlessness appear.
Early detection allows timely treatment with supplemental oxygen, potentially preventing severe complications.
Pulse oximeters are widely available without prescriptions at pharmacies and supermarkets.
Accuracy Considerations for Darker Skin Tones
Pulse oximeter readings can sometimes be less accurate in individuals with darker skin due to light absorption differences. Studies show that readings may overestimate true oxygen levels in Black individuals.
To improve reliability, take multiple readings throughout the day and track trends over time.
Alternatives to Pulse Oximetry
If you lack a pulse oximeter, monitor for rapid heart rate (60-100 bpm normal) and breathing rate (12-20 breaths per minute normal), which may indicate low oxygen.
Consequences of Low Blood Oxygen
Low oxygen levels can impair bodily functions and may cause symptoms such as:
- Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion
- Restlessness
- Chest pain
- Rapid breathing and heart rate
- Dizziness
- High blood pressure
- Vision problems
- Poor coordination
- Euphoria
Hospital Treatments for Low Oxygen
Oxygen therapy is the primary treatment, often delivered via nasal cannula—thin tubes placed in the nostrils connected to an oxygen source. This helps restore normal oxygen levels and eases lung strain.
Oxygen flow is adjusted as you recover, with gradual reduction until you no longer require supplemental oxygen.
Recognizing Medical Emergencies with COVID-19
While many experience mild symptoms, severe COVID-19 requires immediate care if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest pain or pressure
- Confusion or speech difficulties
- Inability to stay awake
- Pale, gray, or blue lips, nails, or skin
In critical cases, intubation may be necessary, placing a tube into the windpipe to maintain airway patency and deliver oxygen directly. Patients may transition from intubation to nasal cannula before discharge.
Discharge plans vary based on overall health, age, lung conditions, and COVID-19 lung damage.
Boosting Oxygen Levels at Home
To support healthy oxygen levels during recovery, consider:
- Quitting smoking to improve oxygen circulation
- Sleeping on your side or stomach with supportive pillows instead of flat on your back
- Practicing pursed-lip breathing to ease breathlessness
- Sitting upright with back support to enhance lung expansion
- Ensuring fresh air by opening windows or spending time outdoors
- Taking short walks to improve circulation and oxygenation
Always follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions, especially if prescribed home oxygen therapy.
Summary
COVID-19 can cause dangerously low blood oxygen levels, requiring prompt medical intervention. A pulse oximeter is an essential tool for home monitoring, helping you know when to contact your doctor or seek emergency care.
For most individuals, oxygen saturation below 95% should prompt a call to your healthcare provider, and levels under 90% demand immediate emergency attention.
Discover the latest news and current events in Sexual Wellness as of 29-05-2022. The article titled " 2025 Pulse Oximeter Guide: How to Monitor Oxygen Levels at Home with COVID-19 " provides you with the most relevant and reliable information in the Sexual Wellness field. Each news piece is thoroughly analyzed to deliver valuable insights to our readers.
The information in " 2025 Pulse Oximeter Guide: How to Monitor Oxygen Levels at Home with COVID-19 " helps you make better-informed decisions within the Sexual Wellness category. Our news articles are continuously updated and adhere to journalistic standards.